Table of Contents
What is Camber In Road?
Camber is the cross slope given in the pavement in a transverse direction to drain out the rainwater from the road’s surface.
Typically, a camber is constructed on the straight roads by upraising the carriageway centre concerning the edge, making the highest point at the centre.
In the case of superelevation at the horizontal curve, the surface drainage is modified by upraising the outer edge of the road concerning the inner edge while providing the specified superelevation.
The cross slope or camber or cross fall rate is typically indicated by the ratio (1: n), which means the slope in the transverse direction is in ratio 1 vertical to n horizontal.
Cross slope or camber is also designated in percentage. For instance, if the cross slope or camber is 2.5%, that means the cross fall is 1 in 40.
Purpose of Providing Camber in Road
The primary purposes of providing camber in the pavements are as follows:
- To drain off or remove rainwater from the surface of the pavement.
- To block the access of water into the layer of bitumen.
- To stop the entrance of water to the subgrade of the road.
- For quick drying of the road surface after rainfall, to avoid accidents due to skidding.
- To assure the quality performance and durability of the road.
Types of Camber In Road
Generally, four types of cambers are used based on the type of pavement surface.
Barrel Camber
The barrel camber is constructed with a continuous curve that may be parabolic or elliptical. In barrel camber, the surface shape is kept steeper near the edge and flat in the middle part.
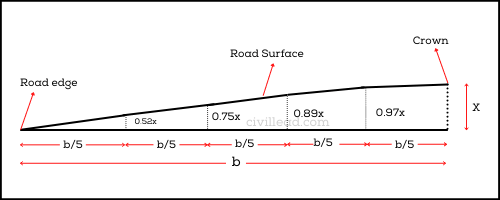
Barrel camber is suitable for the roads with fast-moving vehicles because they frequently cross the centre or crown due to overtaking.
Sloped Camber or Straight Camber
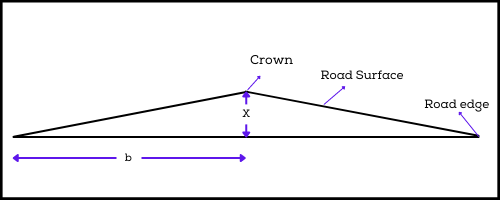
Sloped camber is constructed with two straight slopes merging at the centre. It is suitable for rigid pavement surfaces such as concrete roads that are relatively impervious.
Two straight line camber
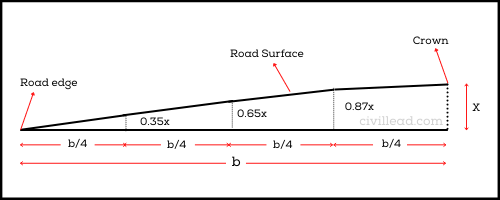
When a camber is constructed with two straight lines flatter near the crown and steeper near the edge, it is called two straight-line camber.
Composite camber
It is the combination of barrel and sloped camber constructed with two straight slopes with parabolic at the centre.
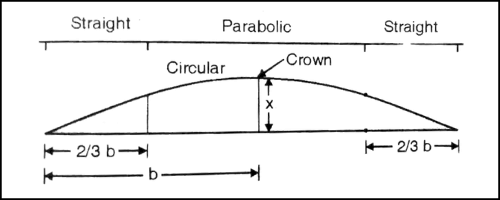
Composite camber is suitable for the road with slow-moving vehicles like iron-tired carts, bullocks carts. The iron tire decreases the contact pressure.
Rate of Camber
Considering the surface type and the quantity of rainfall in the locality, the minor camber required to drain the surface water may be determined. The too steep camber causes the following undesirable effects on the traffic.
- The excessive camber causes uncomfortable side thrust and drags on the steering of the automobile. Also, the unnecessary thrust on the wheel along the road edge causes unequal wear of the tyre.
- During overtaking operations, excessive camber causes discomfort to the occupants.
- Excessive camber causes the problem of overtopping to highly laden bullock carts.
- Crosscuts are more pronounced because of the rapid flow of water.
- As it is comfortable to drive near the centre line, this portion wears out quickly.
The values of recommended camber for various types of road surface by IRC are as follows.
| S.No. | Surface Type | Crossfall/Camber Heavy Rainfall | Crossfall/Camber Low Rainfall |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cement Concrete or thick bituminous surface | 2% ( 1 in 50 ) | 1.7% (1 in 60 ) |
| 2 | Thin Bituminius Surface | 2.5% (1 in 40) | 2% (1 in 50 ) |
| 3 | WBM, Gravel | 3% ( 1 in 33) | 2.5% (1 in 40) |
| 4 | Earthen | 4% ( 1 in 25) | 3% (1 in 33 ) |
Method of providing camber
- Firstly suitable value of the camber is determined based on the type of road.
- Then the subgrade is prepared as per the desired shape of the camber by rolling.
- The rolling should be carried out from the edge toward the centre.
- Finally, the camber is checked with the help of a camber board or template. A board of specified thickness is cut in desired camber shape, and a metal sheet such as an iron sheet is fastened to the bottom, and the cross profile of the camber is checked.
Calculation of Camber in Road
By straight edge method
Suppose Carriageway width is 3 meter
half-width = 1.5 meter
Considering Value of N = 6 cm or 0.06
Camber = 0.06/1.5×100
= 4% or 1:25
By Level Method
RL of LHS = 98.60 m
RL of Centre = 98.620
RL of LHS = 98.55
Average of LHS and RHS RL = 98.575
Difference of Level = 98.620 – 98.575 = 0.045
Camber = 0.045/1.5×100
3% or 1:33
Advantages of Camber
- Camber makes the pavement durable by draining out the water from the road surface.
- Camber blocks the formation of a water pool on the road surface to eliminate the subgrade damage due to water percolation.
- Camber allows smooth traffic flow and prevents accidents due to skidding by draining water from the road surface and making it dry quickly.
Also, Read
What is WBM Road? – Construction Procedure of WBM Road
Material Required For The Construction of WBM Road
Concrete Road vs Asphalt Road – Which Is Better?
Density of Cement, Sand and Aggregate, Bulk Density of Aggregate