Table of Contents
What Is Cavity Wall?
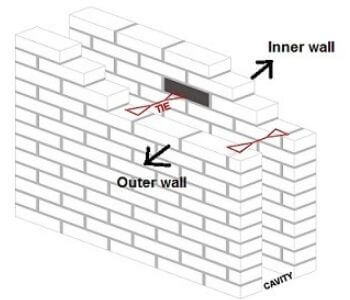
It is a wall made of two parallel levels of masonry, separated by a continuous air space. Continuous space is called a cavity. Cavity walls consist of three main parts:
- The outer leaf which, is the exterior part of the wall
- The cavity, the continuous open-air space
- The inner leaf, which is the interior part of the wall
Purpose of Cavity Walls
The cavity walls are provided for the following purpose:
Damp Prevention
The cavity wall eliminates the penetration of moisture from the outer leaf to the inner leaf and thus helps keep the inside of the building free from dampness.
It is made possible because whatever moisture gets penetrated through the outer leaf is subjected to evaporation by the air inside the cavity, as cavities are kept well ventilated.
Thermal Insulation
The air in the cavity acts as a non-conductor of thermal heat and minimizes the transmission of heat from the external face of the interior leaf. Thus cavity walls, help greatly in the thermal insulation of the buildings.
Sound Insulation
The air in the cavity wall acts as a cushion for absorbing sound. By adopting cavity walls building may be rendered soundproof as considerable external noise gets absorbed in the cavity.
Efflorescence
As dampness is not allowed to penetrate by a cavity, the inner wall of the cavity, which is always a load-bearing wall, is kept free from the efflorescence effect.
Economy
Cavity walls are found to cost about 20% less than the construction of the same thickness solid wall.
Size And Location of Cavity Wall
The cavity between two leaves should not be less than 50 mm and not more than 75 mm. The cavity may be sealed, or ventilated sealed cavity is more effective for thermal insulation.
In contrast, ventilated one is more effective for damp prevention ventilation of cavity by using air brick in the outer leaf near the bottom and top of the cavity.
The cavity may be started from the top of the foundation concrete block, but it is seen that the cavity below the damp proof course does not serve any purpose.

Hence up to 100 to 300 mm below D.P.C. at plinth level, brickwork in the foundation is generally constructed solid, and the cavity may be started only about 150 mm below the D.P.C. level.
This 150 mm depth below D.P.C. helps draw any condensed moisture below the level of D.P.C. Damp proof course for the two leaves of the wall is set on an individual basis, goodbye at an equivalent level.
The cavity may lead right up to the top of the parapet and be converted by copying and D.P.C. It may be stopped levels, but D.P.C. must be laid over the cavity.
Constructional Details of Cavity Wall
The cavity walls have two leaves, inner and outer, with hollows spaces in between them. The width of the cavity varies from 50 mm to 75 mm.
The thickness of the outer leaf of the wall, which is generally a non-load-bearing wall, is half-brick. The inner wall is always load-bearing, and its thickness should not be less than one brick.
Wall ties or bonded bricks connect the two parts of the wall. Metal wall ties are spaced at horizontal intervals of about 0.90 mm and vertical intervals of 450 mm.
The wall tie should be arranged in a staggered fashion. The outer wall is always in a stretcher bond, but it can be constructed in other bonds using brickbats.
I hope now you have enough information about the cavity wall. Please, don’t forget to share it.
Thanks for reading this article.
Also, Read
Standard Brick Size – Importance, Types and Tolerance
AAC Blocks – Properties, Advantages, Disadvantages and Laying Process
Brick Bond – Types, Difference Between English Bond and Flemish Bond
Difference Between Brick Masonry and Stone Masonry