Table of Contents
Difference Between Bitumen And Tar
The terms “bitumen,” “tar,” and “asphalt” are frequently used interchangeably. However, they have distinct characteristics that must be considered before application. They’re black, sticky, and suitable for road construction.
Bitumen is mainly found naturally, whereas tar must be distilled. Bitumen is typically found in solid form, whereas tar is in liquid form.
When bitumen is mixed with inert materials, asphalt is formed. Asphalt comes in two varieties: natural asphalt and rock asphalt.
This article will explain the difference between bitumen and tar.
What is Bitumen?
Bituminous materials are hydrocarbon mixtures, either natural or hydrogenous, or a combination of the two;
that can be found in gaseous liquid, semiliquid, or solid form and are completely soluble in carbon disulfate.
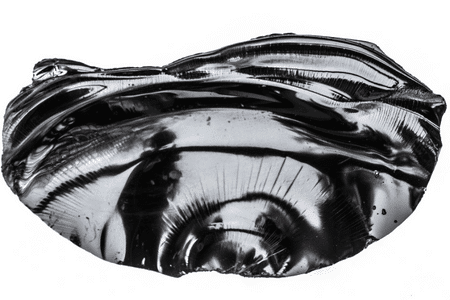
According to the Indian Standard Institution, bitumen is a non-crystalline or viscous material with adhesive properties;
that originates naturally or through a refinery process originates from petroleum and is considerably soluble in carbon disulfide.
Bitumen is a dark brown or black substance. It can occur naturally or be obtained as a by-product of petroleum distillation.
Asphalt is formed when bitumen is mixed with inert materials. Natural asphalt and rock asphalt are two types of asphalt.
Properties of Bitumen
- It is usually solid or semi-solid, black, and sticky.
- When exposed to heat, it melts or softens.
- It has a specific gravity of 1.09.
- Carbon disulfide completely dissolves it.
- It functions as a binder in all asphalt types.
- It has high chemical stability but oil affects it.
- It has a low permittivity and a high insulation resistance.
Uses
- It serves as a damp-proof course for basement walls, swimming pools, urinal lining, and other structures.
- It is used to fill up the joints in leaky roofs because it creates a solid expansion joint.
- It is commonly used in road construction.
- It is used in the production of heat-insulating materials for buildings.
- It also produces cold-moulded bituminous plastics, roofing felt, and impermeable paints. Bituminous paints are created by mixing red, green, or brown pigments into the asphalt. These paints are appropriate for both decorative and waterproof flooring.
What is Tar?
It is a viscous liquid produced by the destructive distillation of wood or coal without oxygen. Coal tar is widely used for road construction because it is superior to wood tar. The tar production process can be divided into three stages:
- To obtain crude tar, coal is carbonised.
- Crude distillation
- To obtain the desired road tar, distillation residue is blended.

Tar is classified into five groups based on its viscosity and other properties: RT-1, RT-2, RT-3, RT-4, and RT-5.
Because of its low viscosity, RT-1 can be used for surface painting in freezing weather.
Under normal Indian conditions, RT-2 is recommended for standard surface painting.
RT-3 can be used for surface painting, light carpet renewal coats, and premixing top course chips.
RT-4 is commonly used to mix macadam in the base course.
RT-5 is used in the grouting process.
Uses
- It is used to construct roads and roofs.
- Bituminous paints and waterproofing compounds are made with it.
- The application of coal tar preserves timber.
- It is applied to the walls of restrooms.
Difference Between Bitumen And Tar
| S.No. | Bitumen | Tar |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | It is black to brown (deep black) in colour. | It is also black to brown (Jet black) in colour. |
| 2 | It is a natural petroleum product formed in a pure or nearly pure state. | It is made by destructively distilling wood or coal without air. |
| 3 | It neither coats aggregates well nor retains them well in the presence of water. | It coats and retains aggregate more quickly in the presence of water. |
| 4 | It has better weather resistance properties. | It has poor weather resistance properties. |
| 5 | Its viscosity is not much susceptible to temperature variation, or bitumens are less susceptible to temperature variation. | Its viscosity varies dramatically with temperature. |
| 6 | It has less free carbon. | It has a higher concentration of free carbon. |
| 7 | Bitumen has a low level of toxicity. | Tar has a high level of toxicity. |
| 8 | Bitumen has less adhesive properties than tar. | Tar is the most adhesive substance. |
| 9 | Bitumen hardens quickly. | Tar takes longer to set than bitumen. |
| 10 | Bitumen gradually loses volatile matter as it expands and thus hardens. | Tar hardens very fast because it loses volatile matter faster as it expands. |
| 11 | Bitumen forms naturally. | Distillation is used to produce tar. |
| 12 | Bitumen is highly durable. | Tar is far less durable than bitumen. |
| 13 | Bitumen degrades much more slowly than tar. | When exposed to weather conditions, the deterioration rate increases. |
| 14 | Bitumen has lower specific gravity. | Tar has a high specific gravity. |
| 15 | Bitumen creates a highly slippery surface. | Tar creates a less slick surface. |
| 16 | The viscosity of bitumen is low. | Tar has a high viscosity. |
| 17 | Bitumen is an expensive material. | Tar is a less expensive material than bitumen. |
| 18 | It is more water and acid resistant. | It has a lower resistance to water and acid. |
| 19 | Bitumen is frequently solid. | Tar is a thick, viscous liquid. |
Final Words
Bitumen and tar are two materials that are frequently used in construction. They do share some characteristics, such as being both dark organic liquids.
They both absorb water from the ground. Bitumen and tar are frequently used in the same areas for construction sealing. There are, however, significant differences between the two.
Also, Read
Difference Between Wood And Timber
Difference Between Ceramic And Vitrified Tiles
Difference Between Veneer And Laminates
Difference Between MDF And Particle Board