Table of Contents
What is Well Foundation?
Wells and Caissons are large-diameter foundations adopted in an underwater situation such as bridge foundations in rivers.
Caissons are large width foundations which carry the load of the superstructure through a layer of weak soil to firm stratum at considerable depth.
Unlike pile foundations, which rarely have diameters greater than 2 meters, caissons can have a width ranging from 10-30 meters and can be founded at depths of 40 m or more.
Caissons are used extensively in the river and marine underwater construction. in particular, they are used as foundations for bridges.
Caissons are usually prefabricated above the ground level and above the water level and sunk to the bearing level as one single unit.
when the process of fabrication and sinking proceed simultaneously they are referred to as well foundation.
Why Well Foundation Is used?
In situations where due to scouring or bearing capacity considerations, foundations are to be taken to greater depths than 5 to 7 meters, open excavation becomes costly and uneconomical due to the following reasons:
- To retain the sides, heavy timbering is required.
- Due to greater earthwork involved due to side slopes, progress in open excavation will be very slow.
- The excavated material refilled in the open excavated foundation leads to loose soil which can be easily scoured.
Thus to rectify above defects well foundations are adopted. In India, well foundation is the most common type of deep foundation.

Generally, the following two types of well foundations may be adopted. In India, wells are generally constructed of brick or stone masonry, while in the western countries iron is used for foundation construction known as tabular foundations.
Panjab System – In this type of foundation deep well foundations are provided without flooring for protection against scouring.
Madras System – In this type of foundation shallow well foundations are provided with continuous flooring both upstream and downstream against scouring.
Also Read – What is Pile Foundation? Types of Pile Foundation
Advantages of Well Foundation
- It can withstand large lateral loads and moments which occur in the case of bridge piers, abutments, towers and tall chimneys.
- It can resist the effect of scouring due to its large cross-sectional area.
- It reduces vibrations and has less noise because the foundation is based, on piers there are fewer vibrations which will disturb the structure.
- Its depth can be, decided due to the sinking process.
- No need for pile cap, since the piers are filled, with concrete, there is no need for a pile cap.
- It is economical, the cost of drilling and installing a caisson is less as compared to traditional foundation.
- They are easily adaptable in various site conditions. It is easy to put caisson at any place. The most difficult, thing to place them is drilling the hole.
Disadvantages of Well foundation
- It can not be constructed, on contaminated sites due to the high amount of drilling required to place the caisson. There is a risk of further contamination throughout the site.
- Experts are necessary for the construction of this type of foundation.
- Lack of skilled worker familiar with this type of foundation.
- Its construction procedure is sensitive, especially placing caisson.
- Lack of qualified inspectors, to inspect the construction of a caisson foundation to ensure that, they are safe and secure.
Also, Read – Grillage Foundation – Types, Advantages and Disadvantages
Types of Caissons
1. Box Caisson
A caisson which is closed at the bottom but can be open or closed at the top.
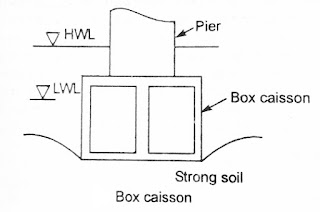
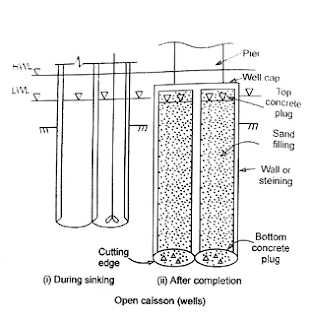
2. Open Caisson or Well
A caisson which is open at the bottom as well as at the top.
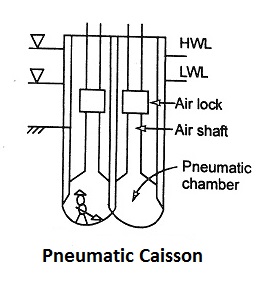
3. Pneumatic Caisson
An open caisson with a chamber at the bottom for maintaining high air pressure.
Also, Read – Combined Footing – Definition and Types
Shape or Types of Well foundation
Different shapes of wells that are commonly used are as follows:
1. Circular Well – These are more commonly used shape is circular, as it has high structural strength and is convenient in sinking. the chance of tilting is also minimum in this type.

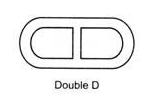
2. Double-D Wells – They are generally used for the piers and abutments of bridges which are too long to be accommodated on a circular well of 9 m diameter.
3. Double Octagonal Wells – These are better than the double-D wells in many respects. The square corners are eliminated and bending stresses are considerably reduced.
However, they offer greater resistance than double-D well against sinking on account of increased surface area. Moreover, the construction is more difficult.
4. Twin-Circular wells – These are two independent wells placed, very close to each other and having a common well cap. the wells are sunk simultaneously.
These wells are suitable where the length of the pier is considerable, which cannot be accommodated on a double -D or double-octagonal well.
5. Rectangular Wells – They are generally used for bridge foundations having depth up to 7-8 m. for large foundations, double-rectangular wells are used.
For piers and abutment of very large size, rectangular wells with multiple dredge holes are used.
Also, Read – Types of Foundations & Footings And Their Uses
Choice of Particular Shape
The choice of particular shape depends the following factors:
- Dimensions of the base of piers and abutments
- The cost and ease of sinking
- Tilt and shifty considerations during the sinking
- Horizontal and vertical forces acting on the well.
Forces acting on well foundation
Generally, the following forces act on a well foundation:
Vertical Forces
- Self-weight
- Buoyancy
- A dead load of the superstructure
- A dead load of bearing and piers
- Live load transferred through the piers
Horizontal Forces
- Braking and a tractive effort of the moving vehicle.
- Force on account of the resistance of the bearing against movement due to change in temperature.
- Force due to flowing water.
- Wind pressure.
- seismic force.
- Earth pressure.
- centrifugal forces.
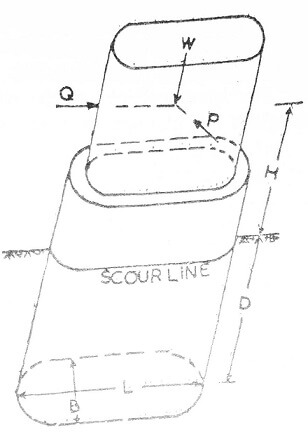
Direction, magnitude and point of application of all the above forces can be determined under the worst possible states. These force can be replaced by horizontal forces P and Q and vertical forces W.
- P = resultant of all horizontal forces in the direction across the pier.
- Q = resultant of all horizontal forces in the direction along the pier.
- W = resultant of all vertical forces.
Also, Read – What is the Purpose of Providing Foundation?
Construction Process
A Well foundation can be constructed on the dry bed or after making a sand island. At a location where the depth of water is greater than 5 m to 6 m and the velocity of water is high.
Well can be fabricated on the river bank and then floated to the final position and grounded. Once the well has touched the bed, sandbags are deposited around it to prevent scour.
The well may sink into the river bed by 50 to 60 cm under its on weight. Further sinking operation is similar to the sinking of a well in a dry bed.
The well is sunk into the ground to the desired level by excavating through the dredge holes.
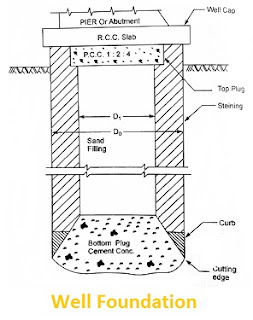
Component of Well Foundation
1. Cutting Edge – It provides a comparatively sharp edge to cut the soil below during sinking operation. It usually consists of mild steel equal angle of side 150 mm.
2. Curb – It has a two-fold purpose. During the sinking, it acts as an extension of cutting edge and also provides support to the well steining and bottom plug while after sinking it transfers the load to the solid below. it is made up of reinforced concrete using controlled concrete of grade M200.
3. Steining – It is the main body of well. It also serves a dual purpose. It acts as a cofferdam during the sinking and a structural member to transfer the load to the soil below afterwards.
The steining may consist of brick masonry or reinforced concrete. The thickness of staining should not be less than that given by equation.
t = K( H/100 + D/10)
Where
t = minimum concrete steining thickness
H = Well depth below the bed
D = External diameter of well
K = A constant
For soft clay 1.25 for hard clay and 1.3 for hard soil with the boulder. The brickwork steining should be about 10 cm more than that the corresponding concrete steining.
4. Bottom Plug – After the well has been sunk to the final position, the bottom plug is formed by concreting. The bottom plug functions as the base of the well.
5. Sand Filling – It utility is doubtful. It is supposed to afford some relief to the steining by transferring directly a portion of the load from well cap to the bottom plug.
6. Top Plug – The opinion is divided about the top plug. It at least functions as a shuttering for laying well cap.
7. Reinforcement – It gives strength to the structure during sinking and service.
8. Well Cap – It is needed to transfer the loads and moments from the piers to the well or wells below.
The shape of the well cap is similar to that of well with a cantilevering of about 15 cm. Whenever 2 or 3 wells of small diameter are needed to support the substructure.
The well cap should be extended to cover the wells. The well cap is designed as a slab resting over the well or wells with partial fixity at the edge of the wells.
Thanks for reading this article. If you find this article helpful please, don’t forget to share it.
Also, Read
Difference Between Plinth Level, Sill Level and Lintel Level
What is Lap Length? How to Calculate it? – Complete Guide
What is Development Length? – Complete Guide
What is Plinth Beam? – Plinth Protection, Difference Between Plinth Beam and Tie Beam