What is Monolithic Slab?
The meaning of the word Monolithic is “made of a single large mass”.
The foundation constructed by pouring a single layer of concrete to construct a slab or footing is known as Monolithic Slab Foundation.
In the monolithic slab construction during the concrete pouring, the outer sides are kept thick, approximately 1 to 1.5 feet, to act as the footing for the load-bearing wall and avoid the footer while the rest of the slab thickness is kept 4 to 5 inches.
Since the construction process of this slab is completed in a single pour of concrete, it offers faster construction and keeps the labour cost low compared to other foundations.
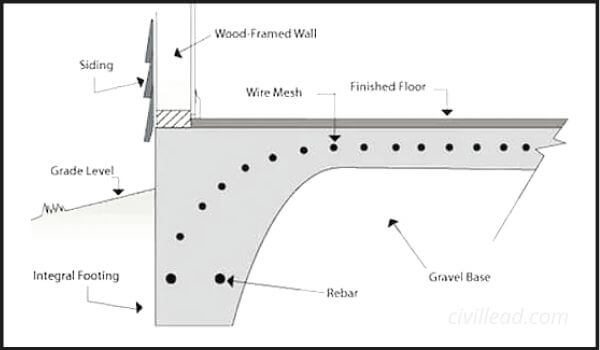
Monolithic slab foundation can be as stable as stem wall foundation when used at the right place and in idle situations.
A monolithic slab foundation is suitable If the ground is level and well compacted throughout the entire property with a low slope.
Severe problems can occur when the conditions are not favourable to this foundation. It is not suitable when the ground requires a lot of fill and dirt since the concrete is susceptible to crack if the ground is not well compacted.
It is not preferable for the houses that require to be made up to rise above a floodplain. In such conditions, the monolithic slab may crack nearby the perimeter walls and other important load-bearing areas.
These cracks can create structural problems which affect other aspects of the house.
Also, Read - Flat slab - Types, Uses, Structure, Advantages And Disadvantages
What is a Floating slab?
A concrete slab that is laid over the ground without anchoring refers to a floating slab.
Since it simply sits on the ground and can move above the frost line as a monolithic unit, that’s why it is called a floating slab.
Since the floating slabs don’t connect with the foundation, it is also called a monolithic slab.
Insulation can help to reduce the movement due to frost depending upon the project’s need.
Mainly it is used as a foundation base for garages, workshops, drive sheds, additional room for home, cottages, etc., on the soil with low bearing capacity.
A floating slab is suitable and economical for the area, with no need for a standard foundation.
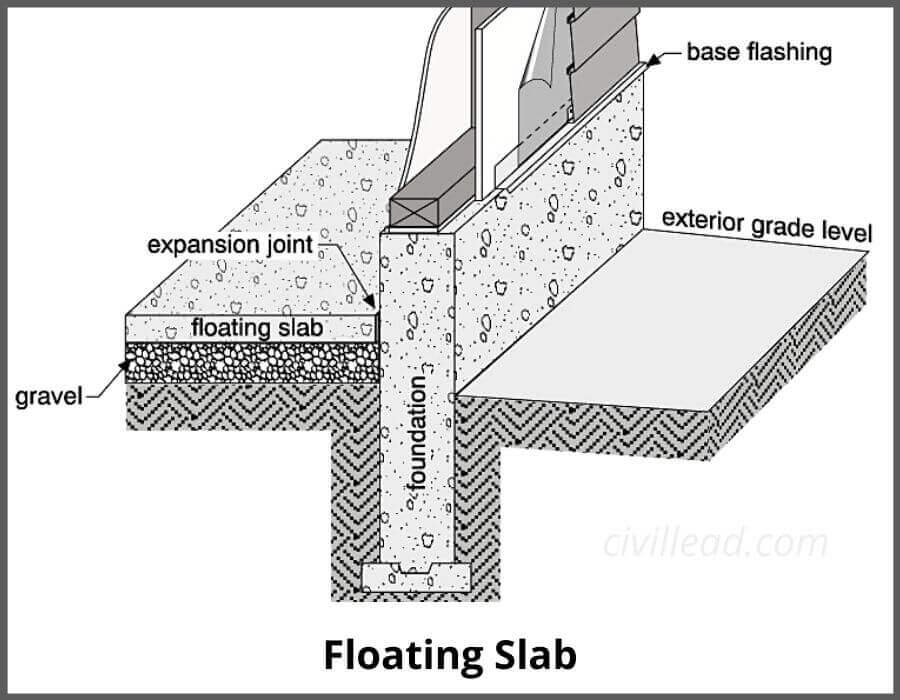
A floating slab contains thickened reinforced perimeter but doesn’t have frost footing. It is suitable for the house extension and garages, which doesn’t need a huge foundation.
Construction of a traditional foundation requires strap footing with a frost wall above it. The strap footing is provided below the frost level, generally 4 feet from grade.
The cost of a strip footing with a frost wall is more because more excavation, concrete, and labour are needed.
Since these buildings have lightweight structures, this foundation is an idle and economical choice.
But the floating slab doesn’t allow basement and underground access due to the loss of storage space. The absence of a basement may also reduce the resale value of the house.
Also, Read - What is Slab Beam|Flat Beam|Hidden Beam|Concealed Beam?
Monolithic Slab Vs Floating Slab
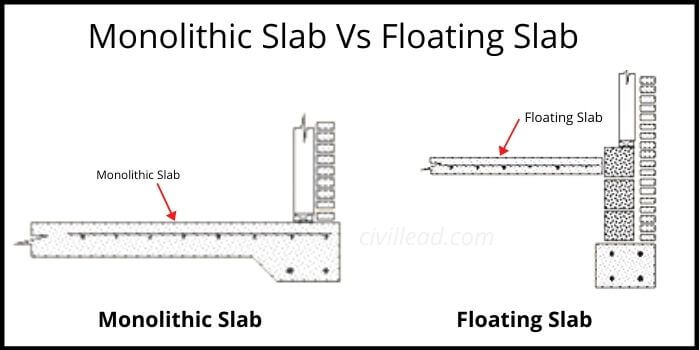
The construction process of floating slab requires two stages; first, the footings are poured separately, and then the floating slab is poured after the footings curing. In contrast, the monolithic slab is cast in a single pour of concrete.
Floating slabs are idle for house addition and garages on the soil with low bearing capacity. In comparison, the monolithic slabs are suitable for the level and well-compacted ground with a low slope.
Monolithic slabs are economical as compared to floating slab since it offers faster construction and requires fewer labours.
I hope now you understand the difference between monolithic slabs and floating slabs. If you like this article and find it valuable, please share it.
Thanks!
Also, Read –
Sunken Slab – Uses, Advantages And Disadvantage
Concrete Mix Ratio – Types, Proportioning of Concrete Mix and Methods
Cracks In Concrete Slab – Why do they develop after the next day of casting?
How to Calculate Quantity of Steel in One Way Slab?