Table of Contents
What is a Flat Slab?
A reinforced concrete slab that generally does not use beams and transfers the load directly to the supporting column refers to the flat slab.
A flat slab gives a plan ceiling surface providing better diffusion of light, simple constructability with the saving in the formwork, shorter story height or considerable headroom, and pleasant appearance.
These slabs are directly held on a suitably spaced column with or without drop panel and column heads. Considering the possible load transfer mechanisms.
It can be imagined that the domain 1-1-1-1, described as the middle stripe (MS), caries load in two ways action with column strips (CS) 2-1-1-2 and 3-1-1-3 providing supports.
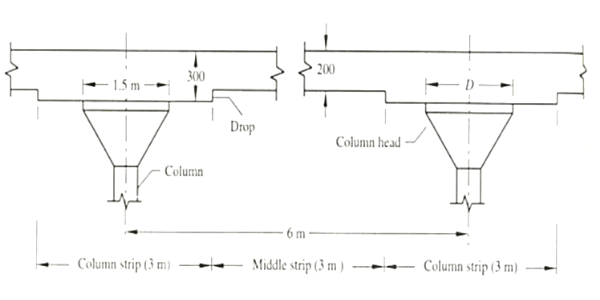
The column strips, in turn, transfer the loads to the columns by one-way action. The column strips function as shallow beams within the slab thickness.
The zones near columns are subjected to high negative moments and shear forces.
For heavy loads and large span, the structural demands direct the slab’s thickened portion around the column called drop and a widened profile at column top identified as the capital or column head.
In flat slab column tends to punch through the slab due to punching shear, which can be eliminated using the below methods:
- Adopting a drop panel and a column capital
- Adopting a drop panel without a column capital
- Utilizing a column capital without drop panel
In such slabs, columns are provided with an extended head known as capital or column head. For carrying heavy loads, the thickness of the slab over columns increases, and the thickened part of the slab is recognized as a drop panel.
For light load, drop panels and the column heads are omitted. Such slabs with uniform thickness supported on the prismatic column are called flat plates.
Also, Read - Sunken Slab - Uses, Advantages And Disadvantages
Types of Flat Slab
- Flat slab including drop panel
- Flat slab including a column head
- Flat slab including drop panel and column head
- Flat slab excluding drop panel and column head

Structural Requirement For Flat Slab
Drop
The drop, when implemented, should be rectangular in plan, and the minimum length of the drop in every direction should not be less than one-third of the panel’s length in that direction.
For exterior panels, the drop’s width at right angles to the discontinuous edge and measured from the column’s centerline should be equal to one-half the drop’s width for interior panels.
The drop panel increases the shear strength of the slab with minimum interference, increases the negative moment capacity of the slab, and stiffens the slab, thus reducing the deflection.
The minimum thickness of the drop panel slab is usually taken 1.25 times the thickness of the slab.
Uses of drop panels :
- It helps to increase the shear strength of the slab floor.
- It helps to increase the flat slab’s negative moment capacity.
- It stiffens the flat slabs, consequently reduces deflection.
Column Heads
Generally, the column head size should keep approximately one-fifth of the span. However, where the column heads are given, the part of a column head that lies within the most significant pyramid with a vertex angle of 90° or right circular cones can be included entirely within the column. For the design direction, a column head outline should be considered.
The column head increases the shear strength of the slab and reduces the moments by reducing the clear span ln.
When the load is heavy, and the span is long, a two-way joist or grid system, commonly known as a waffle slab, may be used.
Such waffle slabs must use solid panels acting as drop panels around the columns. The size and shape of the solid part depend on the requirements of shear and moment.
Beams can also be formed, eliminating a row or two of waffles on the column centerline. Alternatively, the long span can have a flat banded slab.
The bands or wide beams are provided 1.5 to 2.0 times as deep as the slab and as wide as necessary up to the width of the column strip. The use of this practice is, however, limited.
Uses of Column heads :
- Column heads help to increase the shear strength of the slab.
- It helps to reduce the clear span and also moment in the slab.
Slab Thickness
Stiffness consideration usually controls the thickness of the flat slab, represented in the ratio of span to effective depth.
However, for computing the modification factors for tension reinforced, the effective percentage of steel across the entire width of the panel at mid-span should be used.
For slabs with drops, as mentioned earlier, the long span to effective depth ratio can be applied directly, whereas, for other cases, the ratio shall be multiplied by 0.9.
The appropriacy of thickness has to be determined for shear and bending moments. The flat slab should have a minimum thickness of 125 mm.

Uses of Flat Slab
- These slabs are primarily useful for parking garages, ramps, highrise buildings, hotels, and industrial structures.
- These slabs are also suitable where the use of beams is restricted.
- These slabs are mainly applicable where structure requires less formwork.
Also, Read - Difference Between Singly and Doubly Reinforced Beam
Advantages of flat slab
Engineers use flat slabs in multiple buildings because of their benefits over other conventional RCC floor systems in different cases. Essential services of flat slabs are given below:
- The flat slab system offers flexibility in room layout, and the Partition wall can be constructed as per need. It also provides a variety of room layouts to the owner and avoids the false ceiling requirement.
- Since a flat slab offers more straightforward reinforcement detailing, it is more effortless to place.
- Such slabs need less formwork. Use extensive table formwork to provide faster construction.
- Since flat slabs don’t need beams, floor height can be minimized, reducing the building height. Also, reduce the load on the foundation. It can save approx 10% of the vertical member.
- Due to the use of extensive table formwork, it requires less time to construct it.
- A flat slab allows the use of a prefabricated mesh of standard size, requiring less installation and better quality control.
- Since the beams are absent in the flat slab, it is easier to install sprinklers and pipes for other use.
- They provide a better appearance and offer better diffusion of light.
- They provide better fire resistance than a conventional floor system.
- It offers faster construction provides economy in the overall cost of the building.
Disadvantages of Flat Slab
Having many benefits of the flat slab also has some disadvantages, which are as follows.
- It has span limitations. It doesn’t offer a large span.
- They are not suitable for masonry partition of brittle nature.
- It uses drop panels that may interfere with oversized mechanical ducting.
- They have middle strip deflection, which may be critical.
- They have more thickness as compared to typical RCC Slabs.
Also, Read
Difference Between One way and Two way Slab
How to Calculate Quantity of Steel in One way Slab
Cracks in Concrete Slab – Why do they develop after casting?
Bar Bending Schedule (BBS) – Importance, Advantages, Preparation
What is an Estimate? – Importance, Estimate of Building in Excel
What is BOQ? – Purpose, Importance, Advantages & Disadvantages