Table of Contents
What is Stair?
A structure with a series of steps affords up and down between the floors or landings known as stairs.
The enclosed place in which the stair is placed is known as the staircase. The area or opening owned by the stair is called a stairway or flight of stairs.
A stair contains treads, risers, stringers and balusters, and so many other relevant components.
Stairs may be constructed from brick, stone, timber, steel, and reinforced cement concrete.
Flight of Stairs
A connected series of steps without any break between the landing and floor is called a flight or stairway. Usually, people call it stairs.
It is called the flight of stairs because the flight symbolizes the “journey toward up” by using feet only without wings.
It divides the large vertical distance into the small vertical distance in the form of steps. A minimum 3 number of steps should be in a flight, and the maximum should not be more than 15.

Stairs are an essential element of the buildings. Without stairs, it won’t be easy to climb to the building’s top.
Although elevators and escalators are available for this purpose which are convenient, stairs offer great exercise that is good for health.
Stairways have various forms straight, half turn, spiral, round, etc. they can be constructed in multiple straight pieces located at an angle and joined by landings.
The stairway consists of multiple steps. Each step consists of a tread and riser. The horizontal part of the step you step on is called trade, while the vertical portion between trades is called the riser.
Characteristics of Good Staircase
A good staircase should have the following characteristics.
- It should have a sufficient size, not too large nor too small.
- The step of the stair should be sufficiently wide.
- It should be near all the rooms of the building.
- The stairs should be solid and durable.
- The riser should not be higher than 20 cm.
- The slightest inclination for the stair is 25 degrees and the highest is 45 degrees.
- A minimum 3 number of steps should be in a flight and a maximum of 15.
- It should have a sufficient landing area.
- It should be located centrally in residential buildings and near the main entrance in public buildings.
- It must have handrails.
Also, Read – 11 – Requirements of Good Staircase
Types of Stairs
- Straight Stairs
- Turning Stairs
- Quarter Turn Stairs
- Half Turn Stairs
- Dog-legged Stairs
- Newel stairs
- Open Well Stair
- Bifurcated stairs
- Geometrical Stairs
- Circular Stairs or Helical Stairs
- Spiral Stairs
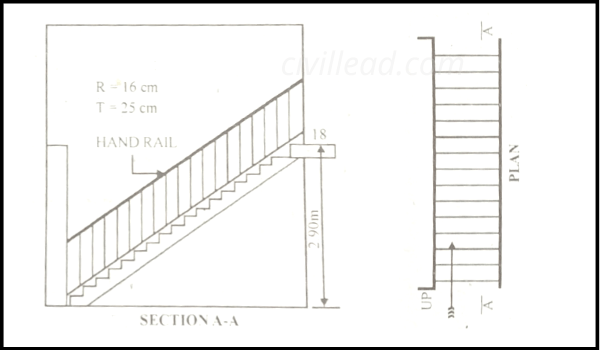
Straight Stair
A stair with parallel steps and risers in the same direction is known as a straight stair. It has only a single flight or two or even more in its length, divided by a landing.
Turning Stairs
In this type of stairs, flights take turns. Types of turning stairs are as follows:
Quarter Turn Stairs
Stairs that turn through one right angle are called quarter-turn stairs.
Half Turn Stairs
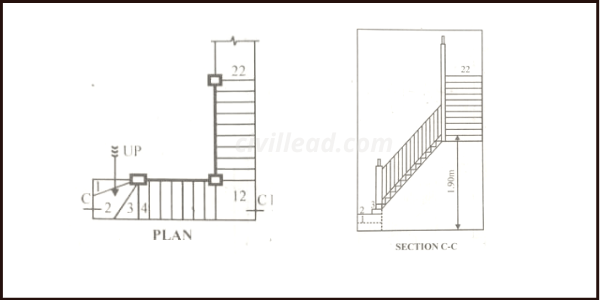
Stairs that turn in 180 degrees, then they are called half-turn stairs. Newel stairs, open-well stairs, and dog-legged stairs are the types of half-turn stairs.
Dog-legged Stairs
Since it’s bent or crooked round in fancied resemblance to the dog’s leg, it is called a dog-legged stair.
It is suitable for restricted going and when the width of the available space is equal to two flights’ combined width.
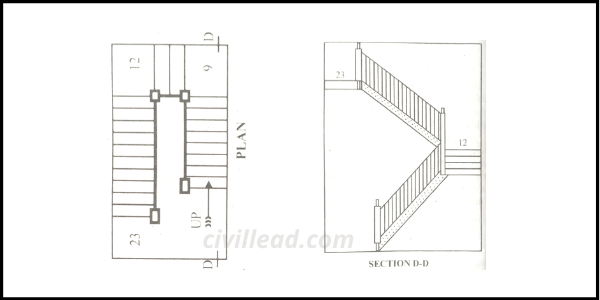
In this type of stair, successive flights rise in opposite directions. The flight of the stair may be separated by:
- A half-space landing
- A quarter space landing
- Two sets winder and no landing
One should avoid the first method as far as possible as it makes the stair too steep and dangerous near the newel post.
Newel Stair
The other name for dog-legged stair is a newel stair because it forms an essential part of the structure. A newel is generally placed at the foot and head of the stairs each flight.
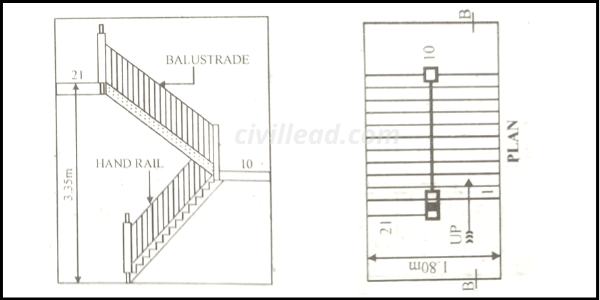
Open Well Stairs
This type of stair is similar to a dog-legged stair, accepting a rectangular hole or opening between flights. Hence the stair’s width will be the sum of two times the step width plus the width of the well.
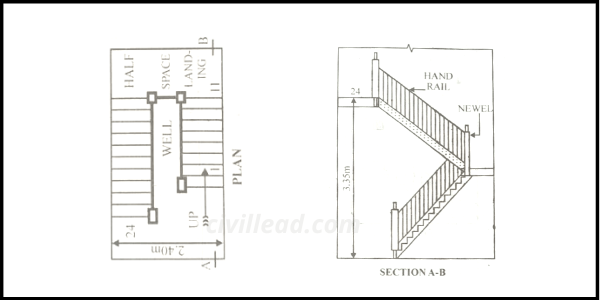
Newels are installed at the head and foot on each stair flight, forming a notable point for the stair to be declared a newel stair. It is a convenient form of the stair, and the well hole allows top lighting.
An open well stair provides satisfying results, so one should try to provide an open well stair, although it needs a little more space than a dog-legged stair.
Bifurcated Stairs
This stair is common in a public building in which it appears like a noticeable feature.
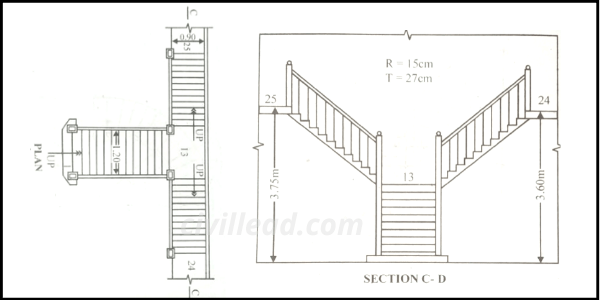
This type of broad stair flight is divided at a landing into two narrower flights which branch off to the right and left.
Geometrical Stairs
These stairs consist of a hole or opening between the flights(backwards and forward).
These stairs have either geometrical form, and they don’t need a newel post. The handrail of geometrical stairs continues without interruption and any angular turn.
In this type of stair, both the string and rails are continuous and set out according to geometrical principles.
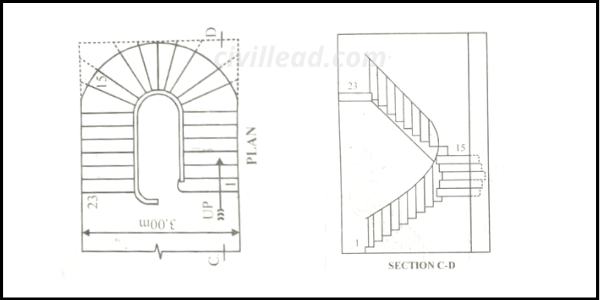
These stairs need a little more width, but space for length is similar to dog-legged stairs.
The direction change is gained by the winders radiating from the curve’s centre of curvature between the flight.
Circular Stairs
Circular stairs are constructed of winders, and there are two forms of circular stairs spiral stairs and circular geometrical stairs.
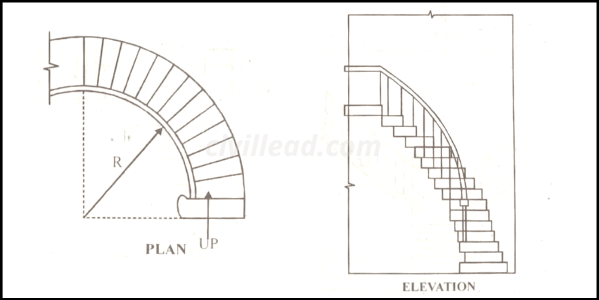
These stairs are usually given at the building’s backside to render access to its various floors for service purposes. This type of stair is mainly constructed in RCC and iron etc.
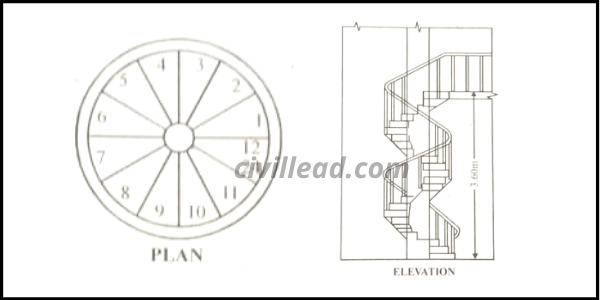
Spiral Stair
In these stairs, all the steps radiate from a standard centre or newel post. They are made up of wood, steel, or concrete. It is provided where the available space is less.
I hope now you have adequate knowledge about types of stairs and flight of stairs. Please share this information.
Thanks!
Also, Read
House Construction Cost Calculator Excel Sheet
9 – Difference Between English Bond and Flemish Bond
Pop Vs Putty – Difference Between Pop and Putty
Standard Room Sizes & Their Location In Residential Building
Estimate of Building Work – Long Wall Short Wall Method, Centre Line Method