Table of Contents
What is a Pitched Roof?
A roof has inclined surfaces at an angle from a central ridge that slopes down, generally in two parts but sometimes in one region only, known as a pitched roof. The vertical rise to horizontal span ratio defines its slope as the roof’s pitch.
This roof is most widely used in the plane area for roofing considerable spanned structures like warehouses, factory buildings, workshops, etc.
A pitched roof is cheaper than any other type. This roof can be made from timber, structural steel, RCC(reinforced cement concrete), and prestressed concrete.
The roofs are sloping or pitched when their inclination angle exceeds about 10 degrees with the horizontal.
The slope angle is maintained lower if wind and rain conditions are not unbearable and snowfall is not probable to occur.
As the situation of wind, rain, and snowfall evolves more and more crucial, the roof slope is raised proportionately.
Types of Pitched Roof
- Single Roofs
- Lean to roof
- Coupled Roof
- Couple-Close Roof
- Collar Roof
- Scissors Roof
- Double or Purlin Roofs
- Trussed Roofs
- King Post Truss Roof
- Queen Post Truss Roof
- Mansard Truss Roof
- Composite Truss Roof
- Truncated Truss Roof
- Belfast Truss Roof
Single Roofs
Lean-to roof or Mono-pitch roof
The most accessible type of pitched roof is shown below in the image. In this roof, rafters are sloping on only one side.
In this type of roof, walls are carried sufficiently higher than others so that the necessary slope to the roof develops.
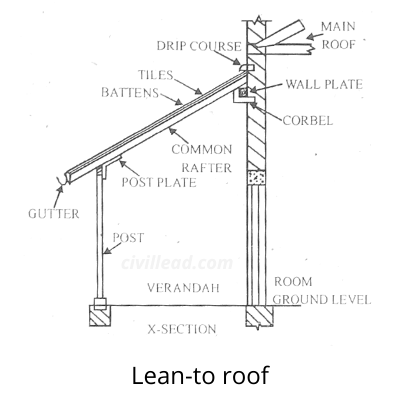
This roof comprises common rafters, and the higher end of the rafters is kept on a wall plate. The lower end of the rafters rests either on a wall plate or fixed to vertical posts and nuts.
The battens are placed across the common rafter, and roof covering is placed over them.
Coupled Roof
The coupled roof is constructed by a pair or couple of inclined rafters sloping on either side of the roof ridge.
The top ends of rafters are fixed to a ridge, and their bottom ends are serrated and fixed to the wooden wall plates inserted in masonry on the walls” top on both ends.
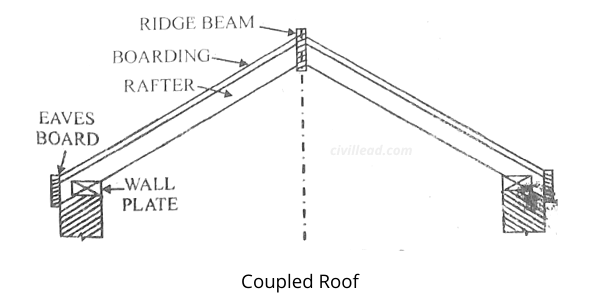
The rafters are placed at proper gaps, and battens are fixed on their top. Lastly, roofing is set on the battens framework.
A coupled roof is suitable for up to a span of 3.6m. This roof is not ideal for large spans as walls are subjected to horizontal thrust.
Couple close roof
This roof is similar to a coupled roof, but it has a tie beam that connects the common rafters near their lower end.
The tie beam carries all the horizontal thrust that was otherwise transmitted to the sidewalls in case of a coupled roof.
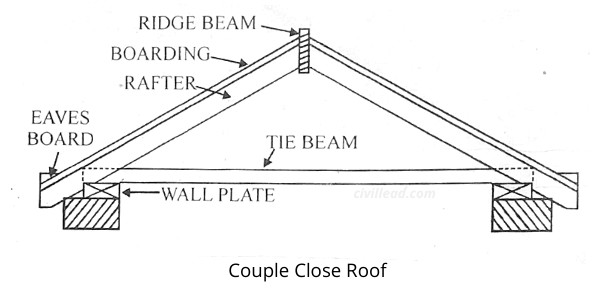
This tendency of the rafter to spread out and the chance of overturning the walls is entirely removed.
This roof is used up to the span of 5 meters. A vertical bar is provided between the tie-beam centre and ridge piece for a greater span.
Collar Roof
Due to raised spans, the rafter of the couple-close roof is prone to bend in the centre. This defect is overcome by fixing the tie beam close to the rafters’ centre, known as the collar roof.
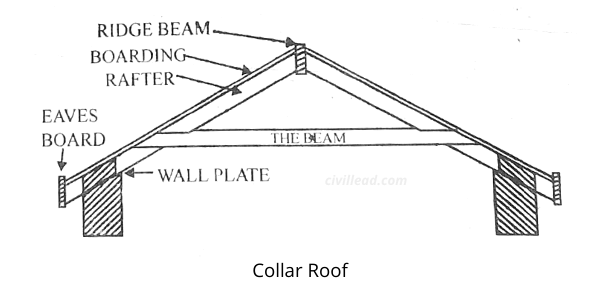
The collar roof provides more height to the room as the ceiling can be fixed to the collar beams and exposed rafters.
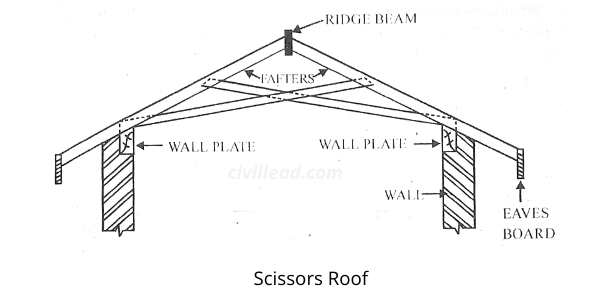
Scissors Roof
The roof has two rafters as in coupled roof. This roof is the same as the collar beam roof.
Still, it has two collar beams intersecting each other to show the appearance of scissors, as displayed in the image below.
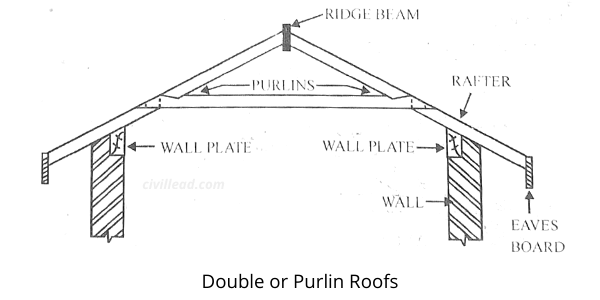
Double or Purlin Roofs
When the span of the roof exceeds 5 meters, the length of the rafter becomes quite long, and thus their size becomes uneconomical.
Thus to reduce the size of the rafters, the intermediate supports known as purlins are introduced under the rafters, as shown in the image below.
Also, Read - What is A Gable Roof? Types of Gable Roof
Trussed Roof
King Post Truss
The king post truss comprises one king post, one tile beam, two struts, and two principal rafters. It is usually used for spans ranging from 5 m to 8 m.
The framework of a truss is built so that its shape doesn’t change under external loads. The trusses are used at a centre distance of about 3 meters.
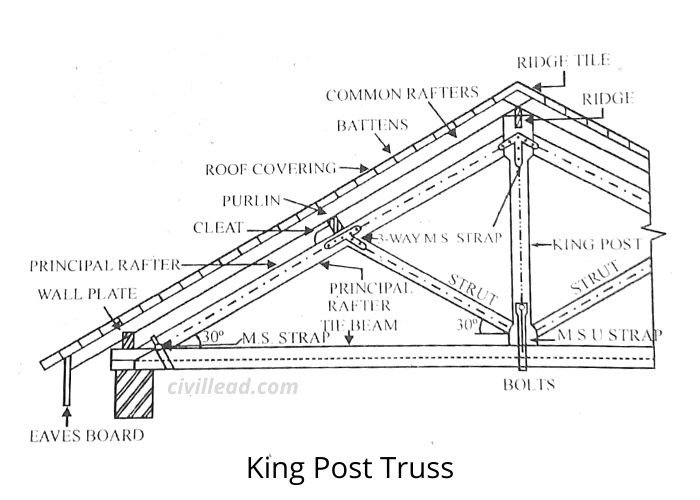
A vertical post located at the centre connects the ridge piece, and the tie beam is called a king post. The struts stop the principal rafter from bending.
Queen Post Truss
Usually, this truss is used in the construction of timber for spans greater than 9 meters and less than 14 meters.
It varies from the king post truss, with two vertical components called queen posts.
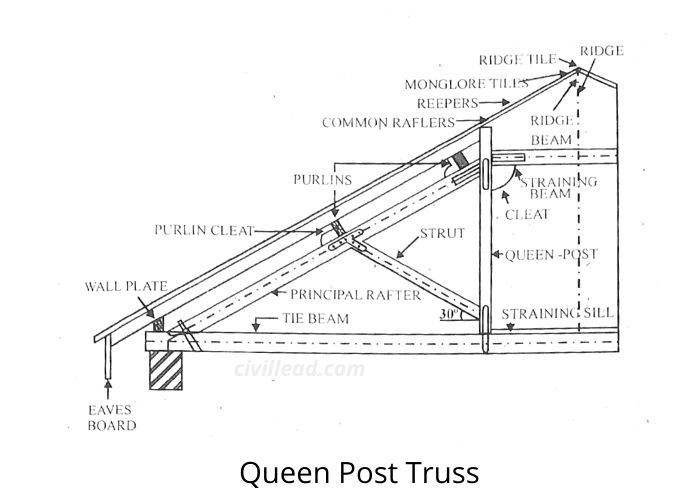
The above image shows the queen post truss. The upper end of the queen posts is kept apart by a horizontal component known as a straining beam.
This beam receives thrust from principal rafters and maintains the joint’s stability.
The inclined struts that the rest of the splayed shoulders transmit to the queen posts are at the bottom and tend to move them inwards.
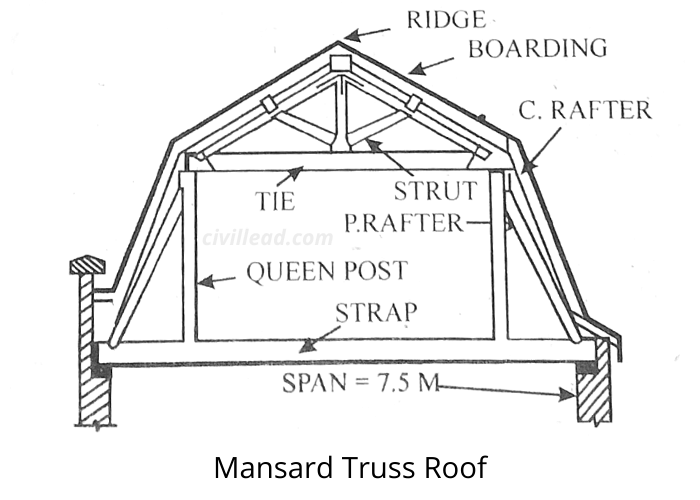
Mansard Truss Roof
This roof is a mix of king post and queen post truss. The low part of the truss is the queen-post type, and the upper part is the king-post type.
The mansard truss has two pitches, the upper pitches vary from 30° to 40°, and the lower pitch varies from 60° to 70°.
Steel Truss Roof
When the truss span is more significant than 10 meters, the use of a steel truss becomes uneconomical. The steel trusses are made by using rolled steel structural members.
The steel trusses consist of angles riveted or welded together through a gusset plate for small spans.
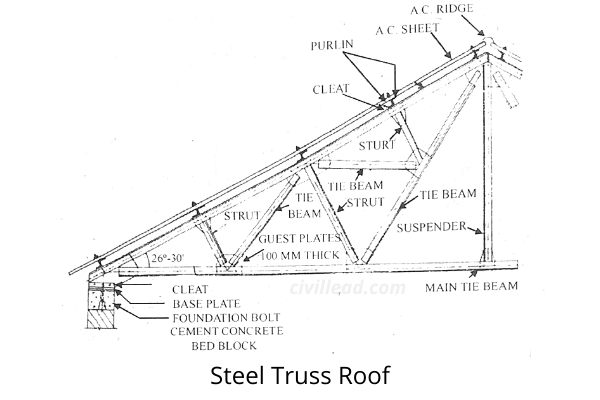
The arrangement and size of different steel truss members depend on the span, loading, and wind pressure.
Composite Truss roof
The trusses made using timber and mild steel sections are known as composite trusses. The compressive members are made of wood and the tensile members of steel.
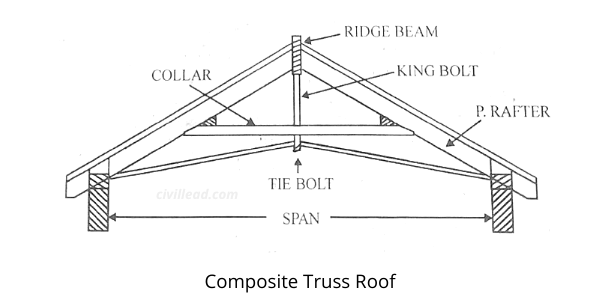
The composite truss is economical and lightweight. Nevertheless, certain filings are necessary at the junction of steel and wood.
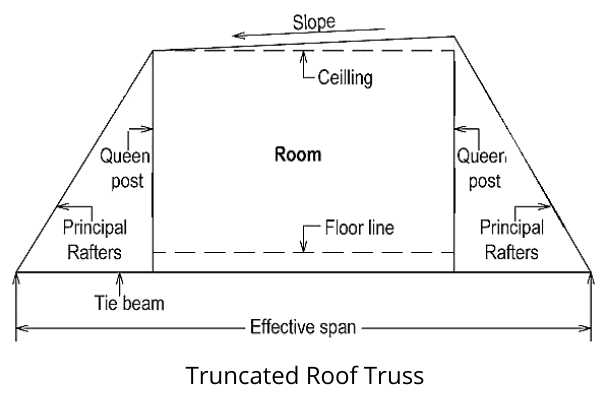
Truncated Truss Roof
It is similar to a mansard truss, but its top is constructed flat with a slight slope to one side. It is provided when necessary to have a room inside the roof.
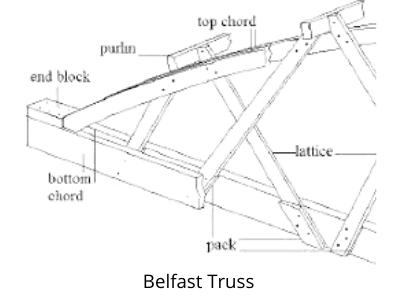
Belfast Truss Roof
Belfast trusses have a top curved surface in a bow shape rather than a sloping side. It comprises thin timber sections with a top curved chord, and a light roof covering is provided at the top. It is suitable for spans up to 30 meters, and it is also called a lattice truss.
Also, Read
8 Types of Stairs, Flight of Stairs
What is Pointing? Type of Pointing, Purpose, Method
Parapet Wall – Purpose, Types & Uses
Standard Room Sizes And Their Location
Monolithic Slab Vs Floating Slab
Plumbing Traps – Purpose, 15 Types of Plumbing Traps